UNC2565: New enhancements to GOOTLOADER malware
The UNC2565 group behind the GOOTLOADER malware continues to improve its code by adding new components and obfuscation techniques to evade detection.
GOOTLOADER is a stealthy malware, classified as a first-stage downloader, designed to target Windows-based systems. It is considered an Initial-Access-as-a-Service (IAaaS) tool used within a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) criminal business model, and uses malicious Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) techniques to worm its way into Google search results and deliver payloads through various methods.
According to a Mandiant report, a new variant of GOOTLOADER has recently been observed that uses a more complex infection chain and additional string variables for a second deobfuscation stage. The UNC2565 group has also been observed using modified versions of legitimate JavaScript libraries to hide their code.
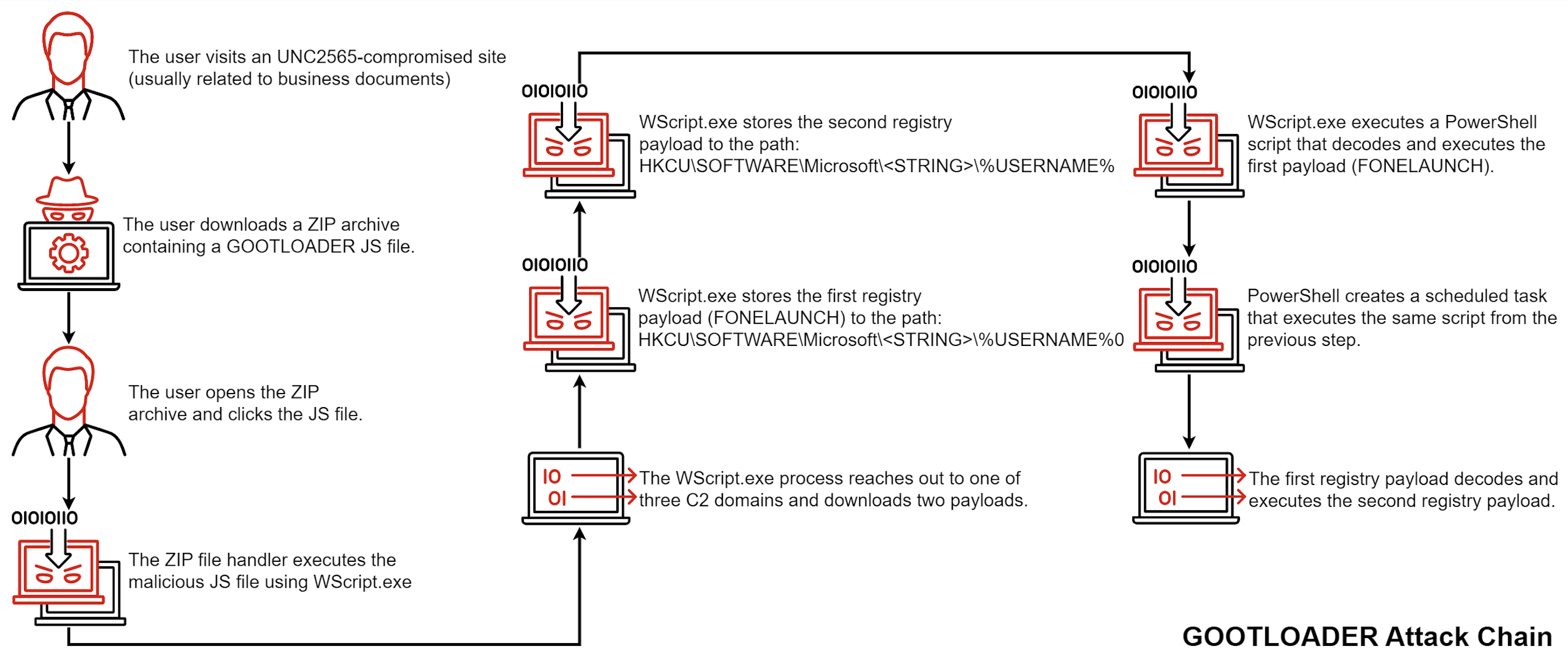
The attack chain begins when a user visits a compromised website and downloads a malicious ZIP archive containing a .JS file. This file ultimately executes the GOOTLOADER malware, which collects information from the infected system and sends it to a command and control server.
The malware also downloads additional payloads, including FONELAUNCH (a .NET-based launcher used to load an encrypted payload from the registry into memory) and Cobalt Strike, which are stored in the registry and run via PowerShell.
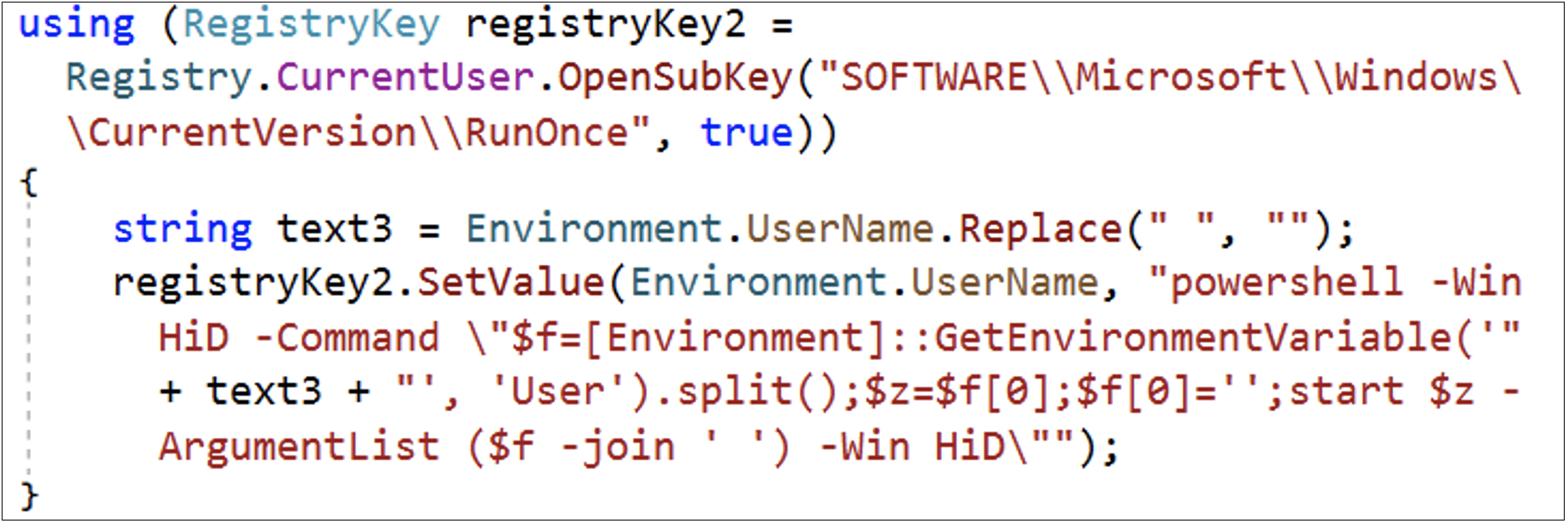
Mandiant’s report also includes Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and YARA rules associated with these threats.