CrowdStrike released the 2023 Global Threat Report
CrowdStrike has released its 9th Annual Global Threat Report, which provides a comprehensive overview of threat actor behaviour, tactics and trends over the past year. The report is based on the activities of more than 200 cyber adversaries and covers a wide range of cybersecurity topics.
Instead of targeting individual organisations, attackers are now targeting the software supply chain, hoping to gain access to larger organisations through third-party software vendors. This approach allows cybercriminals to exploit the trust that organisations have in their software vendors to gain access to sensitive data.
The report also highlights several key findings from the past year. These include an increase in malware-free attacks and interactive intrusions, indicating that human adversaries are becoming more sophisticated at evading traditional antivirus protection.
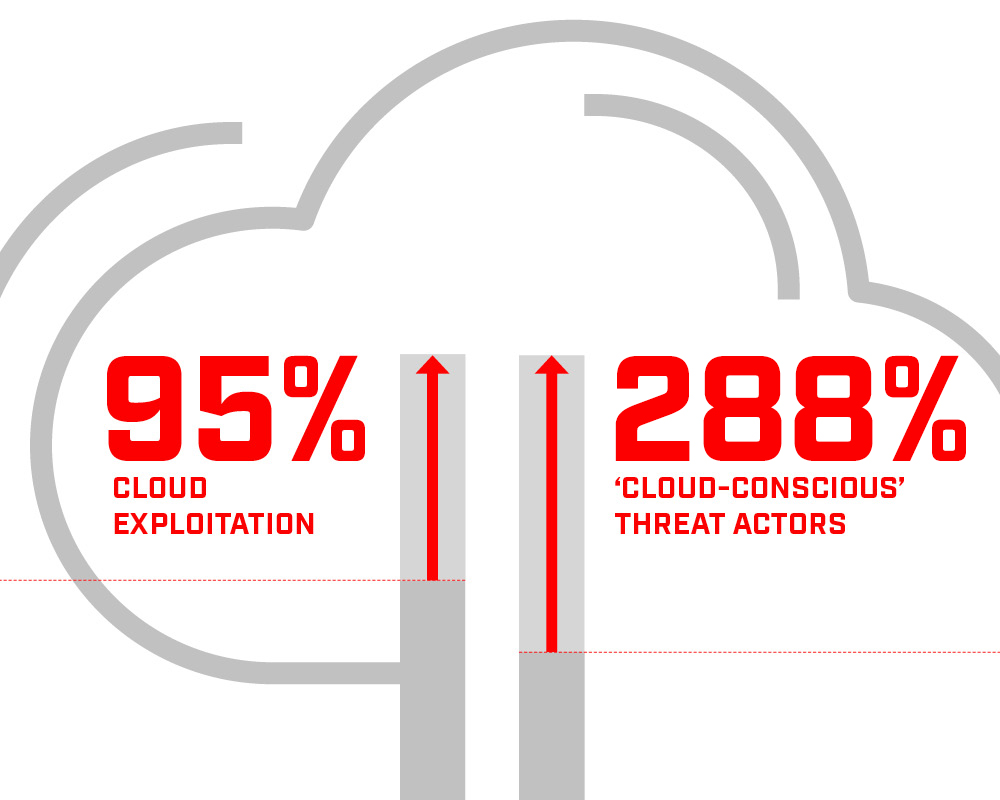
Cloud exploitation also grew by 95%, and threat actors are now moving beyond ransom payments to conduct data theft and extortion campaigns.
Additionally, China-nexus espionage surged across all 39 global industry sectors, while social engineering tactics targeting human interactions, such as vishing and SIM swapping, are on the rise.
Finally, the report notes a decrease in average eCrime breakout time and a re-weaponization of vulnerabilities, including Log4Shell and ProxyNotShell.