Bitwarden vulnerability allows attackers to steal passwords using iframes
The popular open-source password management service, Bitwarden, offers an auto-fill feature that can automatically fill in users’ saved credentials when they visit a website. However, this feature has a potentially dangerous behavior that could allow malicious iframes embedded in trusted websites to steal user credentials and send them to an attacker.
Flashpoint analysts recently discovered this issue while investigating the Bitwarden extension. They found that the plugin could autofill forms defined in embedded iframes, even those from external domains. Although the embedded iframe does not have access to the content of the parent page, it can wait for the login form to be filled in and pass the credentials to a remote server without any further user interaction.
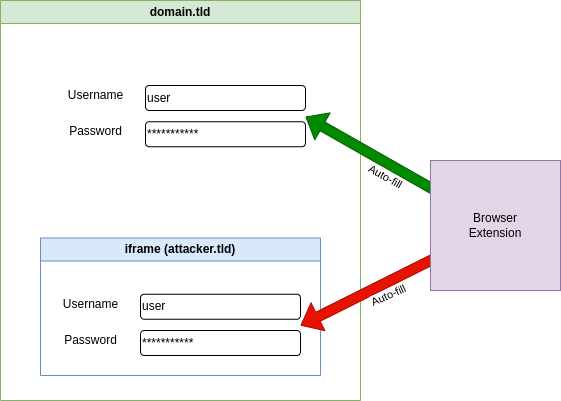
While Flashpoint reported that the number of risky cases was low because iframes were rarely embedded in the login pages of high-traffic websites, they identified a second issue with Bitwarden’s autofill functionality: Bitwarden also autofills credentials on subdomains of the base domain that match a login.
This means that if an attacker hosts a phishing page under a subdomain that matches a saved login for a particular base domain, the credentials will be captured when the victim visits the page if autofill is enabled.
Bitwarden has been aware of this security issue since 2018 but has decided to leave the behavior unchanged. Instead, Bitwarden has added a warning in the software’s documentation and the extension’s associated settings menu.
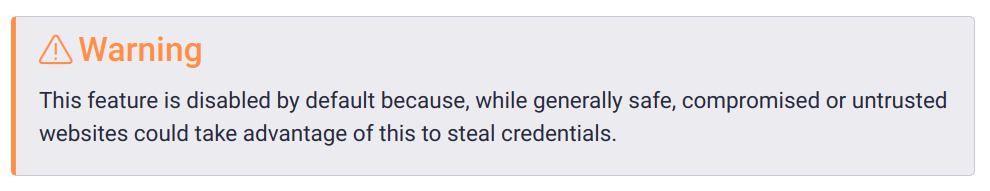
Bitwarden has also promised to block autofill on reported hosting environments in a future update. However, it does not plan to change the iframe functionality.