Researchers discover hardware bug in AMD Ryzen processors that bypasses BitLocker
Researchers from the Technical University of Berlin have discovered an exploit called faultTPM that can bypass security protections like BitLocker by exploiting a hardware bug in the firmware TPM (fTPM) of AMD Ryzen processors based on Zen 2 and 3 architectures.
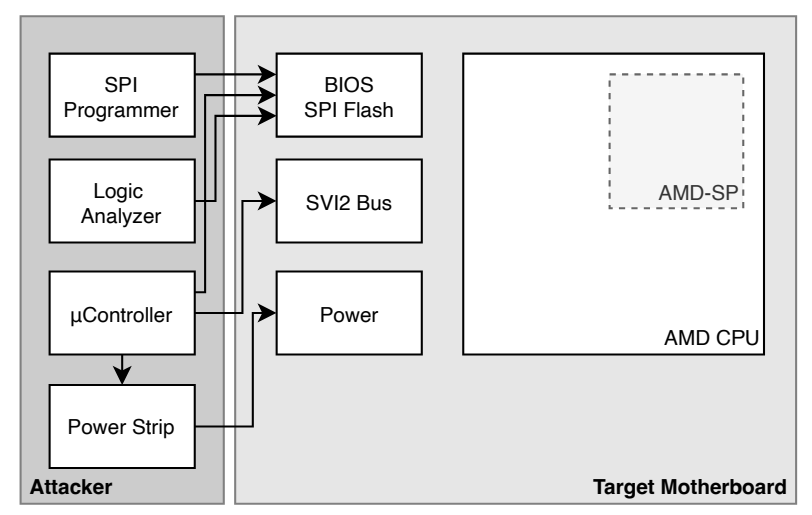
However, the exploit requires physical access to the computer, which makes it unlikely for most users to be affected. The exploit involves a voltage fault injection attack that can access encrypted data in the fTPM, allowing attackers to bypass BitLocker protection.

The attack can only be executed by connecting a specific device that costs around $200 to the Platform Security Processor (PSP) present in Zen 2 and 3 chips.

As it is a hardware bug, it is difficult to solve, and the only solution would be to implement it in future architecture.